The Bone Scan Powerpoint powerpoint version goodversion.ppt
Outline For Bone Scan
I. What is a Bone Scan
-A bone scan is a nuclear scanning test to find abnormalities in the bone
-It is used to diagnose diseases in the bone or that have spread to the bone, locating the sources for bone pain, diagnosing fractures, and dectecting fractures that may not be seen in an x-ray, and detecting damage to bones due to infection or illness
-A tracer (radioactive material) is injected into the blood stream so that when a gamma camera is used, abnormalities can be detected
-The tracer then leaves the body via the urinary system
II. When is a Bone Scan Used
-A bone scan is used when something may be undetecible by a normal X-Ray.
-It will detect fractures that are repairing themselves because the tracers will attach to areas where bone is repairing itself
III. How a Bone Scan Works
-Before a bone scan a lab tech will inject a tracer into the blood stream
-The tracer then attaches to areas where the bone is repairing itself, the rest of the tracer gets flushed out through the urinary system
-The lab techs then do the procedure where the patients has pictures taken of them by a gamma camera however with small lesions a single photon emission computed tomography camera will be used
-The pictures usually take 20-30 minutes to take and the patient will usually return in 2-3 hours for additional imaging
IV. The Dangers of a Bone Scan
-All tests with radioactive tracers have some risk
-Doctors try to limit this risk by limiting the time of exposure
-However if one is exposed too much, diseases can occur
Photos



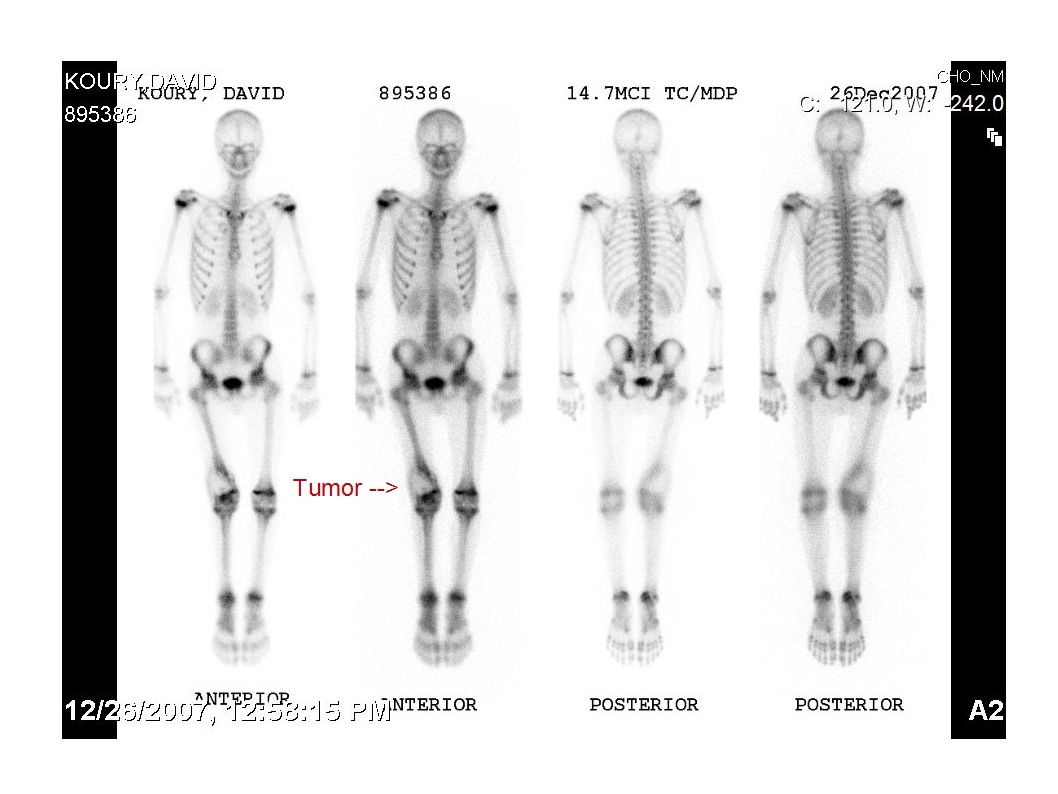





Vocabulary List
Bone Scan- a nuclear test to find abnormalities in the bone
Tracer- radioactive material that is injected into the blood stream
SPECT- Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography
Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography- used to find true 3D information
Cancer- a class of diseases in which a group of cells display uncontrolled growth and sometimes spreads to other parts of the body
Allergy- a disorder of the immune system often referred to as atopy
Gamma Camera- a device used to image radiation emitting isotopes
Compression Fracture- a collapse of the vertebra
Bone Repair- a proliferative physiological process in which the body facilitates the repair of a bone fracture
Urinary System- the organ system that produces, stores, and eliminates urine
Web Sites
Mayo Clinic Bone Scan Risks
http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/bone-scan/MY00306/DSECTION=risks
Mayo Clinic Bone Scan - why its done
http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/bone-scan/MY00306/DSECTION=why%2Dits%2Ddone
Wikipedia Bone Scan
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bone_scan
Wikipedia SPECT Scan
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SPECT_scan
Wikipedia Cancer
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cancer
Wikipedia Allergic Reaction
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Allergic_reaction
Wikipedia Gamma Camera
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_camera
Wikipedia Compression Fracture
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Compression_fracture
Multiple Choice Questions
1. A bone scan is used to diagnose which of the following?
A. Diseases that have spread to the bone
B. Locating the sources of bone pain
C. Diagnosing fractures
D. Detecting damage to bones due to infection or illness
E. All of the above X
2. A tracer is
A. Ink that is injected in to the bloodstream
B. Radioactive material that is injected in to the bloodstream X
C. Water that is injected in to the bloodstream
D. Sedative that is injected in to the bloodstream
E. A and C
3. What system does the tracer leave through?
A. Respiratory
B. Lymphatic
C. Cardiovascular
D. Urinary X
E. Endocrine
How can you detect if there is a problem with the bone?
A. The tracer attaches to the repairing bone X
B. The tracer attaches to the spinal cord
C. If the patient complains of pain
D. A and B
E. All of the above
5. Order of the procedure
I. Patient is injected with tracer
II. The tracer is attached to the bone
III. The test takes place
IV. The photos are read
A. IV, II, III, I
B. III, II, I, IV
C. I, III, IV, II
D. II, I, IV, III
E. I, II, III, IV X
6. What is SPECT?
A. Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography
B. It is similar to conventional nuclear medicine planar imaging using a gamma camera
C. It is able to provide true 3D information
D. It is used when lesions are extremely small
E. All of the above X
7. How do doctors try to limit the risk of a bone scan
A. They only use a tracer when needed
B. They limit the time of exposure to the tracer X
C. They only perform the test when needed
D. A and C
E. B and D
8.What are some of the risks that occur rarely from a bone scan?
A. Cancer
B. Diabetes
C. Allergic Reaction
D. Paralysis
E. A and C X
9. What is NOT a use of a bone scan?
A. Finding fractures
B. Radiation therapy X
C. Finding arthritis
D. Finding unexplained bone pain
E. Finding bone diseases
10. What is a tracer injected into?
A. A vein X
B. An artery
C. A capillary
D. All of the above
E. None of the above

Comments (1)
csnanatomy said
at 11:27 am on Sep 9, 2009
Be a little more specif about what particular problems and occur with too much exposure to radioactive tracers and where in the bloodstream is the tracer injected. Tell us more about SPECT and gamma cameras.
You don't have permission to comment on this page.